Table of Contents
Introduction…………………...……………………………..….3
Post War Economic History……………...................……….....5
- American Cooperation, Trade, Finance & Investment…….…..7
- Integration of the European Union……….…………….............9
- Economic Performance & Policies Of the European Union…..11
- Success in Transitioning Asian Economies.……….…….…….13
- Conclusion …………….……………………….……….…… .16
- References ……………………………………………….……..17
Introduction
So as we move on to the next coursework,” United States, European and Asian Economic System” Or I can Say that I am going to discuss the Economic Systems of the Three biggest continents , the one who controls the world monetary wise.
To start with the economic system? What is Economic System is?
A bookish definition of Economic system is “The ideas and institutions that people draw upon and the behaviors in which they engage in order to secure resources to satisfy their needs and desires”
But Economic System is a smaller word but it is bigger and larger than life. Economic System stands for the country? What its position is in the world market?
Basically, an economic system is a mechanism which deals with the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services in a particular society.
The economic system is composed of people, institutions and their relationships. It addresses the problems of economics, like the allocation and scarcity of resources.
There are several basic questions that must be answered in order to resolve the problems of economics satisfactorily. For example, the scarcity problem requires answers to basic questions, such as: what to produce, how to produce it, and who gets what is produced. An economic system is a way of answering these basic questions
The most basic and general economic systems are:
- Market economy (the basis for several "right-wing" systems, such as capitalism)
- Mixed economy (arguably the "centrist" economic system)
- Planned economy (the basis for several "left-wing" systems, such as socialism)
- Traditional economy (a generic term for the oldest and traditional economic systems)
- Participatory economics (a recent proposal for a new economic system).
A market economy is an economy in which goods and services are traded, ask and bid prices are typically understood to be the result of subjective value judgments. When these prices allign, a trade is made, and exchange price is determined. Bid prices are influenced by competition among buyers and ask prices are influenced by competition among sellers. A market economy that has little or no governmental intervention is called a free market. E.g. is United States of America is a live example of the same, as a pure capitalist country. But some people say it has a mixed economy. Some European Countries do come in Market economy e.g. Switzerland. Japan (Asia) etc
A mixed economy is an economy that contains both private and publically, or state owned or controlled enterprises. A mixed economy contains private ownership of the means of production, infrastructure, and institutions but may also contain state-ownership of some of these things. It allows for private financial decisions by businesses and individuals, but not absolute nor near absolute autonomy, as many of these decisions are otherwise overridden by government. E.g. Some European countries come in Mixed Economy, United Kingdom, Singapore (Asia), India (Asia). Most of the Asian countries either come in this category or Planned economy i.e. Socialist Economy.
A planned economy is an economic system in which decisions about the production, allocation and consumption of goods and services is planned ahead of time, in either a centralized or decentralized fashion. Since most known planned economies rely on plans implemented by the way of command, they have become widely known as command economies. E.g. is Soviet Union and China. Well China has covered a long way to cover the way and they have reached to the market economy level since 1990. And they were widely successful in their vision, until the early 1990s during which both the command economy and the market economy coexisted.
A traditional economy is an economic system in which decisions such as the whom, how, what, and for whom questions are all made on the basis of customs, beliefs, religion, habit, etc. It has an advantage over other systems, in that there is little friction among members because relatively little is disputed. However, it restricts individual initiative and has a lack of advanced goods, new technology, and growth. The Traditional Economic system is used by African tribes and was used by Native Americans. It is also found today in some parts of South America, Asia, and Africa.
Participatory economics, or parecon for short, is an economic system proposed as an alternative to contemporary capitalism and also an alternative to centrally planned socialism or coordinatorism. To implement the decision making principle, a parecon would be organized in consumers’ and producers’ councils. Many individuals would participate in both types of councils.
Geographically, these councils would probably be nested with neighborhood councils, ward councils, city or regional councils and a country council. Decisions would be achieved either through consensus, majority votes or through other means. The most appropriate method would be decided on by each council.
Local decisions like the construction of a playground might be made in the ward or city consumers’ council, probably interacting with both city and countrywide producers’ councils. Countrywide decisions, like the construction of a high-speed mass transportation system, would be discussed by the country consumers’ council, possibly interacting with a city producers’ council in the city where the materials are produced, or countrywide or international producers’ councils
so these are the major five classification of economic system in which the world is divided. Which majorly constitutes United States, European and Asian Countries respectively.
Post War Economic History
The end of World War II to the late 1960s was a golden era of American capitalism. President Kennedy passed the largest tax cut in history upon entering office in 1961. $200,000,000,000 in war bonds matured, and the G.I. Bill caused a well-educated work force. Well Except the United Countries most of the countries were badly hitten by the world war –II , especially European countries and Asian Countries (Japan, India etc)
As Britishers rules India at the time of world war –II they were the whom whose economy was badly hitten due to which they were forced to give independence to Asian Countries.
The U.S. underwent a kind of golden age of economic growth. This growth was distributed fairly evenly across the economic classes, which some attribute to the strength of labor unions in this period. I can say United States really come up after the post world war with some tough competition given by Soviet Union between 1950’s to 80’.
Even after world war over in 1945. The world has faced tensions because of cold war between USA and Soviet Union (1962-1985) especially. After the Gorbachev period came to an end. The economy collapses due to which the Soviet Union has been divided into multiple countries.
Germany who has been divided into east and west which later got united in 1990. That they can take care of their own internal and external affairs.
After world war –II Japan was devasted. All the large cities (with the exception of Kyoto), the industries and the transportation networks were severely damaged. A severe shortage of food continued for several years.
The occupation of Japan by the Allied Powers started in August 1945 and ended in April 1952. General Macarthur was its first Supreme Commander. The whole operation was mainly carried out by the United States.
The 1973 oil crisis shocked the Japanese economy which was heavily depended on oil. The reaction was a shift to high technology industries.
I would like to talk about the crude oil i.e. petrochemical products. Which has been responsible for many wars in the history?
The U.S. petroleum industry's price has been heavily regulated through production or price controls throughout much of the twentieth century. In the post World War II era U.S. oil prices at the wellhead have averaged $20.94 per barrel adjusted for inflation to 2004 dollars. In the absence of price controls the U.S. price would have tracked the world price averaging $22.86. Over the same post war period the median for the domestic and the adjusted world price of crude oil was $17.18 in 2004 prices.
Until the March 28, 2000 adoption of the $22-$28 price band for the OPEC basket of crude, oil prices only exceeded $23.00 per barrel in response to war or conflict in the Middle East.
In 2001 a weakening US economy and increases in non-OPEC production put downward pressure on prices. In response OPEC once again entered into a series of reductions in member quotas cutting 3.5 million barrels by September 1, 2001. In the absence of the September 11, 2001 terrorist attack this would have been sufficient to moderate or even reverse the trend. In the wake of the attack the crude oil price plummeted. Spot prices for the U.S. benchmark West Texas Intermediate were down 35 percent by the middle of November
By 2003, with an improving economy U.S. demand was increasing and Asian demand for crude oil was growing at a rapid pace. The loss of production capacity in Iraq and Venezuela combined with increased production to meet growing international demand led to the erosion of excess oil production capacity. In mid 2002, there was over 6 million barrels per day of excess production capacity, but by mid 2003 the excess was below 2 million.
Crude oil and petrochemical prices was always a worry for the whole world and which has been reasons for many wars too.
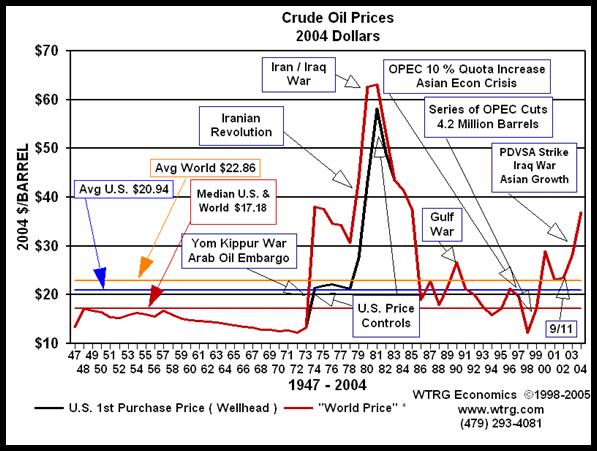
Graph depicting the crude oil prices from 1947 – 2004.
In your opinion whose economy has been badly hurt? Which Economic System gets weaken after world war-II?
I think it was the economic system of European countries which was a base for World War –II. Their economy was badly hurt. Before world war-II. United Kingdom and France was the major powers of the world. And they have a very strong hold on the Asian countries. But World War-II has broken the backbone of these countries.
Their economy has a whole went down. For United Kingdom, their has been a saying that sun never sets in their kingdom. But after world war –II they have to leave their colonies and to make them free. I say world got awakened after world war-II as every country who was fighting for their freedom. Got the freedom in a span of 2-3 years after world war –II.
American Cooperation, Trade, Finance & Investment
The Central & Eastern Europe Business Information Center (CEEBIC) offers a variety of services to the U.S. business community to facilitate trade and investment between the United States and Central and Eastern Europe. This one-stop center for economic and commercial information on Central and Eastern Europe opened in January 1990 and has assisted more than 300,000 companies with questions about this growing market.
The American cooperation to the market has been tremendous, we all know that the world is moving towards globalization. The companies have started moving from one part of the land to capture the market, to sell their product and to earn profits.
The Overseas Private Investment Corporation is an independent U.S. Government agency that sells investment services to assist U.S. companies investing in some 140 emerging economies around the world. It mobilize and facilitate the participation of United States private capital and skills in the economic and social development of less developed countries and areas, and countries in transition from non market to market economies.
The major principles are
a) Insuring investments overseas against political risks.
b) Financing of businesses overseas by loans.
c) Financing private investment funds that provide equity to businesses overseas
d) Advocating the interests of the American business community overseas
For financial assistance, The World Bank Group is the world’s largest provider of development assistance followed by International Monetary funds.
To help underdeveloped countries, to provide assistance to them in their growth
Apart from that there are other bodies also. IFC is the largest multilateral source of loan and equity financing for private sector projects in the developing world. IFC finances and provides advice for private sector ventures and projects in developing countries in partnership with private investors and, through its advisory work, helps governments create conditions that stimulate the flow of both domestic and foreign private savings and investment.
Its particular focus is to promote economic development by encouraging the growth of productive enterprise and efficient capital markets in its member countries. IFC participates in an investment only when it can make a special contribution that complements the role of market operators. It also plays a catalytic role, stimulating and mobilizing private investment in the developing world by demonstrating that investments there can be profitable
IFC's traditional and largest activity is project finance. Using its own funds IFC provides both loan and equity finance to private sector projects that meet IFC's appraisal criteria, but which cannot get financing from other sources on reasonable terms. IFC also offer quasi-equity and financial risk management products. It is important to point out that, although IFC lends on market terms, IFC does not compete with, but rather complements private capital.
America trade policy is also followed by TDA , TDA is a small, independent federal agency. It is primarily involved in agriculture, energy, environment, health care, information technology manufacturing, mining and minerals development, telecommunications, transportation and water resources. TDA funds project planning activities that directly influence the procurement decisions related to major industrial or infrastructure projects in developing and middle-income countries
TDA's main tool for getting U.S. firms in on the "ground floor" of major projects abroad is the funding of feasibility studies. Feasibility studies examine the technical, legal, economic, and financial aspects of a development project in the concept stage. Study grants are signed directly with the host country project sponsor on the condition that an American firm will be selected to perform the study.
TDA also sponsors conferences and reverse trade missions called "orientation visits." Both of these activities familiarize foreign decision makers with American-made products and services, build business relationships, and encourage U.S. companies to export to developing and middle-income countries.
There are so many enterprise funds in the world who takes monetary stakes fromUnited States to prosper. As United States is the one of the most financially and prosperous country in the world.
United States also provide loans to other country for their internal affairs e.g. India and Pakistan. They had so much financial aid from the USA for development in the past recent years. Even they have got so much from the World Bank.
So United States do run a lot of Enterprises to do trade , finances and investments with the rest of the world , after all it has been undisputedly known as the land of opportunities in the world market.
What do you recommend about United States trade, finance and investment policies? Are they really fruitful as it’s seems in the case of Asian countries?
Integration of the European Union
For centuries, Europe was the scene of frequent and bloody wars. In the period 1870 to 1945, France and Germany fought each other three times, with terrible loss of life. A number of European leaders became convinced that the only way to secure a lasting peace between their countries was to unite them economically and politically.
In 1957, European community came into picture. In 1967 the institutions of the three European communities were merged. From this point on, there was a single Commission and a single Council of Ministers as well as the European Parliament
Economic and political integration between the member states of the European Union means that these countries have to take joint decisions on many matters. So they have developed common policies in a very wide range of fields - from agriculture to culture, from consumer affairs to competition, from the environment and energy to transport and trade. The European Union's relations with the rest of the world have also become important. The EU negotiates major trade and aid agreements with other countries and is developing a Common Foreign and Security Policy. It took some time for the Member States to remove all the barriers to trade between them and to turn their "common market" into a genuine single market in which goods, services, people and capital could move around freely. The Single Market was formally completed at the end of 1992, though there is still work to be done in some areas - for example, to create a genuinely single market in financial services
In 1992 the EU decided to go for economic and monetary union (EMU), involving the introduction of a single European currency managed by a European Central Bank. The single currency - the euro - became a reality on 1 January 2002, when euro notes and coins replaced national currencies in twelve of the 15 countries of the European Union (Belgium, Germany, Greece, Spain, France, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Austria, Portugal and Finland).
A basic tension exists within the European Union between intergovernmentalism and supernationalism. Intergovernmentalism is a method of decision-making in international organizations where power is possessed by the member states and decisions are made by unanimity. Independent appointees of the governments or elected representatives have solely advisory or implementational functions. Intergovernmentalism is used by most international organizations today.
An alternative method of decision-making in international organizations is supranationalism. In supranationalism power is held by independent appointed officials or by representatives elected by the legislatures or people of the member states. Member state governments still have power, but they must share this power with other actors. Furthermore, decisions are made by majority votes, hence it is possible for a member-state to be forced by the other member-states to implement a decision against its will.
Some forces in European Union politics favour the intergovernmental approach, while others favour the supranational path. Supporters of supranationalism argue that it allows integration to proceed at a faster pace than would otherwise be possible. Where decisions must be made by governments acting unanimously, decisions can take years to make, if they are ever made. Supporters of intergovernmentalism argue that supra-nationalism is a threat to national sovereignty, and to democracy, claiming that only national governments can possess the necessary democratic legitimacy. Intergovernmentalism is being favoured by more countries like United Kingdom, Denmark and Sweden; while more integrationist nations such as the Benelux countries, France, Germany, and Italy have tended to prefer the supranational approach.
Due to the changing name of the European Union (from European Economic Community to European Community to European Union) suggests, it has evolved over time from a primarily economic union to an increasingly political one. This trend is highlighted by the increasing number of policy areas that fall within EU competence: political power has tended to shift upwards from the member states to the EU.
Major policy areas are which will be covered by European Union to cover different aspects of cooperation.
- Autonomous decision making: Union Member states have granted the European Commission power to issue decisions in certain areas such as competition law, State Aid control and liberalization.
- Harmonisation:State laws are harmonised through the EU legislative process, which involves the European Commission, European Parliament and Council of the European Union. As a result of this European Union Law is increasingly present in the systems of the member states.
- Co-operation: Union Member states, meeting as the Council of the European Union agree to co-operate and co-ordinate their domestic policies.
The tension between EU and national (or sub-national) competence is an enduring one in the development of the European Union
What do suggest about the policies set by European states, will politically they be fruitful for small countries?
I think their policy setting is open and everybody has the right to vote to represent their country so all policies will be set with the majority favouring it.
Economic Performance & Policies Of the European Union
Many of the policies of the EU relate in one way or another to the development and maintenance of an effective single market. Significant efforts have been made to create harmonized standards – which are designed to bring economic benefits through creating larger, more efficient markets.
The power of the single market reaches beyond the EU borders, because to sell within the EU, it is beneficial to conform to its standards. As of now the economic performance is very good in the world market their currency is doing well in the market.
The Policies has been set to keep in mind that should not hit the internal growth of the country. I would like to cover up both internal aspects and external aspects of their policies as it’s the largest economy in the world if considered as a single market.
The Internal policies which were set by the European Union are
1) Free trade of goods and services among EU member countries.
2) A common EU competition law controlling anti-competitive activities of companies.
3) Free movement of capital between EU member Countries.
4) Harmonization of government regulations, corporations law and trademark registrations.
5) A single currency, the Euro (except UK, Denmark and Sweden).
6) Common system of indirect taxation, The VAT and common customs duties and excises on various products.
7) Funding for the development of disadvantaged regions (structural and cohesion funds).
So these are the internal policies which are used by the world’s largest economy (If taken as a single unit)
The External Policies which has been set by European Union are
1) A common external tariff, and a common position in international trade negotiations.
2) Funding for programmes in candidate countries and other Eastern European countries, as well as aid to many developing countries, through its Phare and Tacis programmes, As some eastern European countries as not as developed as Western European countries
3) The establishment of a single market European Energy Community by means of the Energy Community South East Europe Treaty.
So these are the external policies set by the European Union, but apart from Internal and external policies they have some co-operation policies also e.g.
1) Freedom for citizens of the EU to vote in local government.
2) Co-operation in criminal matters, including sharing of intelligence.
3) A common security policy as an objective, including the creation of a 60,000-member European Rapid Reaction Force for peacekeeping purposes.
4) Common policy on asylum and immigration.
5) Common funding of research and technological development, through four-year Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development.
The EU economy is expected to grow further over the next decade as more countries join the union - especially considering that the new States are usually poorer than the EU average, and hence the expected fast GDP growth will help achieve the dynamic of the united Europe. However, It is estimated that the Eurozone will only grow around 0.3 per cent (Q2 2005)
Graph – Population and GDP per capita of EU member states
The EU economy is expected to grow further over the next decade as more countries join the union - especially considering that the new States are usually poorer than the EU average, and hence the expected fast GDP growth will help achieve the dynamic of the united Europe.
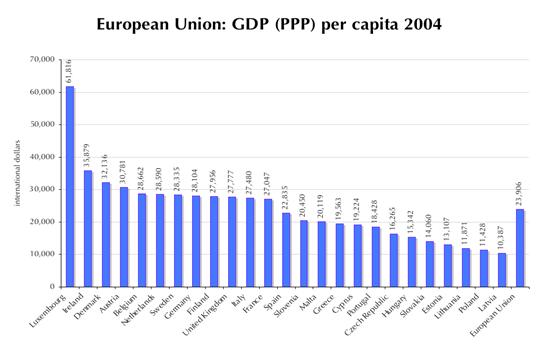
Graph Depicting per capita income of European nations -2004
Success in Transitioning Asian Economies
The world has entered the age of "globalization" or that we live in a "global economy." what does that actually mean? For over fifty years, the world economy has been growing more closely integrated in terms of trade and capital flows. To a great extent, globalization is simply the continuation of that trend. But with greater freedom of trade and investment and new breakthroughs in telecommunication and information technology, markets have become much larger, more complex, and more closely linked than ever before...
Asia has been the showcase of the benefits of globalization. In 1996, private capital flows to developing and transition economies reached an all time high of $235 billion, of which nearly half went to Asia. Some events have shown that some of those funds were not invested wisely. Nevertheless, over the last several decades, the forces of globalization have allowed many countries in Asia to accelerate investment and growth, create more jobs, reduce poverty, and attain other important human development goals
In Malaysia, for example, the share of the population living below the poverty line declined from almost 50 percent in 1970 to less than 5 percent in 2000. In Korea, the literacy rate increased from around 30 percent in the mid–1950s to over 99 percent today.
But if globalization offers many opportunities, it also holds two major risks. The first can be seen in the recent experience of Thailand, Korea, and Indonesia, all of which have suffered major financial crises around few years back, when investors lost confidence in their economies and large capital inflows turned into massive capital outflows. The second risk can be seen in the experience of many African countries. Countries that are unable to participate in the expansion of world trade or attract significant amounts of foreign capital risk becoming marginalized from the global economy and falling farther and farther behind the rest of the world in terms of growth and human development.
I should recommend that in order to be successful in the global economy, countries must first have properly functioning domestic economies. The first is to allow market forces to set prices and allocate resources so that the economy can operate efficiently. Progress in this area has been uneven in Central Asia, particularly in the agricultural sector, and private investment, labor productivity, output, and rural incomes have suffered. Countries that hesitate to liberalize agriculture, or indeed, other sectors of their economies, one key aspect of improving resource allocation—as well as taking advantage of the opportunities in global markets—is to open the economy up to foreign trade and hence to international price signals and competition. Many countries in the Asian region are facing the enormous challenge of making the transition from a centrally-planned to a market-oriented economy. Government officials in these countries need to manage economic policy geared toward free market conditions in a manner that will eventually attain sustainable growth and development. The success of this transition depends, in large part, on the training of future economic managers in these countries. Transition to a market economy is a lengthy process comprised of various spheres of economic activities.
In spite of the high education level of the population, of the intensive care provided by the International Financial Institutions (IFIs) and the support of bilateral donors, the growth rates are low, the inflation rates high, the budget unbalanced and the currencies shaky. The poverty line is rising. The foreign direct investments do not meet the expectations, with the exception of the oil, gas and the gold mining sectors. The external debt is growing rapidly.
In order to make a difference there are certain steps which I feel Asian countries should follow, Their GDP is low and have immense poverty. Most of the countries are still known as under developed countries in Asia. To overcome that reasonably consistent and to achieve a critical mass of reform, local government should convince investors that reform is irreversible, and that the country is truly integrating into the international economy. They should work as a union like European countries have started for the development of all their countries equally. Country like Japan, Singapore and Korea has set an example for other countries to perform their GDP is the among the topmost in the world. East Asia’s success also made a persuasive, and so far enduring, case for the benefits of globalization. It offered strong support for an export-oriented, market-driven model of development. the successful economies in the region opened themselves up to international markets, rejecting protectionism for trade liberalization.
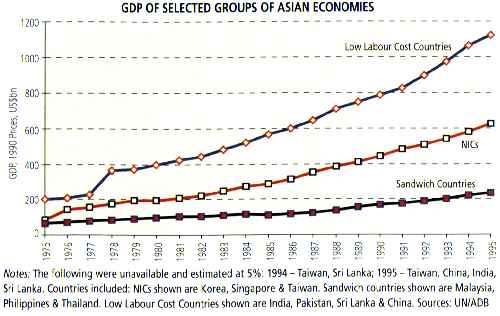
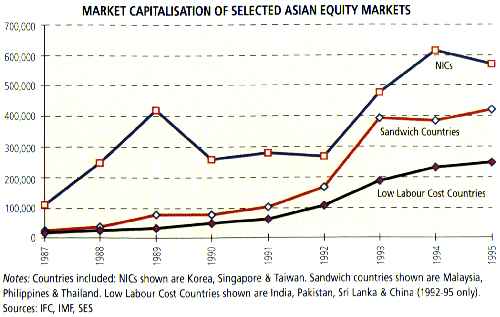
Graphs – i) GDP of Some Asian Countries ii) Market Capitalisation of selected Asian Equity Markets
What is your opinion about Asian Economy? Have they capitalized the resources as European Union or United States did?
I feel most of the countries remained under developed due to the obstacles they have may be due to their caste, religion or race. They never tried t perform to the level as European countries and United States did
CONCLUSION
To conclude my coursework I will say that the all the economic system United States, European and Asian Majorly are coming closer due to globalization, Most of the countries are already very developed in European Union, It’s the Asian country who are rated as under developed and they need to cover up a lot e.g. India has come up very well lot of foreign companies are coming to start their operations.
If I really look from a broader prospective the world economy will has many variations, previously 50- 60 years back United Kingdom was considered to be the known as the most developed country as industrial revolution has taken place. While after world war-II that has been shared by many countries like United States, Soviet Union and Japan
International Business Cycle
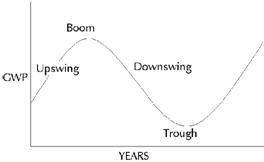
Graph – Showing International Business Life Cycle
The three various factor that control the global economic activity
- Investment flows.
- Monetary conditions.
- Market confidence.

Graph- The growth figures for Advanced and Transition economies
References
Robert Gilpin - Political Science – (2002) War and Change in World Politics (Cambridge University Press:Cambridge,UK)
R A C Parker - History – (2002) The Second World War: A Short History (Oxford University Press Inc: New York USA)
Peter N Stearns - History – (2001) The Encyclopedia of World History (Houghton miftlin company: New York,USA)
Christopher Booker, Richard North (2003) The Great Deception: The Secret History of the European Union (Continuum International Publishing Group : London,UK)
Neill Nugent (2002) The Government and Politics of the European Union (Palgrave Macmillan: New York,USA)
Shalendra D Sharma - Business & Economics –( 2003) The Asian Financial Crisis: Crisis, Reform and Recovery (Manchester University Press:Manchester,UK)
Thomas C Fischer - Business & Economics – (2000 ) The United States, the European Union, and the "Globalization" of World Trade :allies ( Greenwood publishing group Inc: Westport,CT, USA)
