- RESEARCHDistance Learning at AIU is enhanced by vast academic resources and innovative technologies build into the Virtual Campus: Hundreds of self-paced courses with video lectures and step by step lessons, thousands of optional assignments, 140,000 e-books, the Social Media & Networking platform allowing collaboration/chat/communications between students, and MYAIU develop students holistically in 11 areas beyond just academics.
- PROGRAMS OFFERED
- Areas of Study
- Courses and Curriculum
- Open Courses
- Register for a Program
- Associate Program
- Associate in Addiction Counseling
- Associate in Agriculture Food And Resources
- Associate in Anti Terrorism Security
- Associate in Behavior Analysis In Special Education
- Associate in Bioethics
- Associate in Climatology
- Associate in Cultural Theological Communication
- Associate in Culinary Arts
- Associate in Ecotechnology
- View all Associates Programs
- Bachelor Program
- Bachelors in Community Development
- Bachelors in Environmental Science
- Bachelor in Education (B.Ed, BS)
- Bachelors in Economics
- Bachelors in Entrepreneurship
- Bachelors in Financial Administration
- Bachelors in Human Resource Management
- Bachelors in Linguistics
- Bachelors in Nutritional Science
- Bachelors in Occupational Health and Safety
- Bachelors in Psychology
- View all Bachelor Programs
- Doctorate Program
- Doctor | of Biology (PhD)
- Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA, PhD)
- Doctor of Economics (PhD)
- Doctor of Electrical Engineering (D.Sc, PhD)
- Doctor of Finance (PhD)
- Doctorate in International Relations
- Doctorate in Information Technology (D.Sc)
- Doctor of Legal Studies (PhD)
- Doctor of Project Management (PhD)
- Doctor of Sociology (PhD, D.Sc)
- Doctorate in Sustainable Natural Resources Management
- View all Doctorate Programs
- Master Program
- Postdoctoral Program
- Postdoctoral in Animal Science
- Postdoctoral in Anti Terrorism Security
- Postdoctoral in Behavior Analysis In Special Education
- Postdoctoral in Bioethics
- Postdoctoral in Blockchain Technology and Digital Currency
- Postdoctoral in Business Management
- Postdoctoral in Cloud Computing
- Postdoctoral in Computer Engineering
- View all Postdoctoral Programs
AIU offers a wide range of majors in areas including the Arts, Business, Science, Technology, Social, and Human studies. More than 120 degrees and programs are available for adult learners at the associate’s, bachelor’s, master’s, doctoral and postdoctoral level. - VIRTUAL CAMPUS
Distance Learning at AIU is enhanced by vast academic resources and innovative technologies build into the Virtual Campus: Hundreds of self-paced courses with video lectures and step by step lessons, thousands of optional assignments, 140,000 e-books, the Social Media & Networking platform allowing collaboration/chat/communications between students, and MYAIU develop students holistically in 11 areas beyond just academics.
- ALUMNI
The world is YOUR campus!”, that is the message of AIU’s month magazine Campus Mundi. Hear the voices and see the faces that make up AIU. Campus Mundi brings the world of AIU to you every months with inspirational stories, news and achievements by AIU members from around the world (students and staff are located in over 200 countries).
The Growing Threat of Satellite Radio Pollution: Implications for Radio Astronomy

What are the potential long-term impacts of satellite radio pollution on the field of radio astronomy?
How can regulatory frameworks be improved to address the challenges posed by satellite emissions?
What responsibilities do satellite companies have in minimizing their impact on scientific research, and how can they be held accountable?
In light of the growing concerns surrounding satellite radio pollution and its implications for radio astronomy, consider the questions above. Write an essay discussing the potential long-term impacts of satellite emissions on scientific research, the necessity of stronger regulatory frameworks, and the responsibilities of satellite companies in mitigating these effects. Your essay should reflect on the interplay between technological advancement and environmental stewardship in the context of space exploration, and it should provide specific examples to support your arguments. Aim for a well-structured response that articulates your insights and conclusions on this pressing issue.
(Login to your student section to access the AIU Additional Resources Library.)
The Growing Threat of Satellite Radio Pollution: Implications for Radio Astronomy
In recent years, the proliferation of satellite constellations orbiting the Earth has raised significant concerns among astronomers, particularly in the field of radio astronomy. These constellations, spearheaded by companies like SpaceX, OneWeb, Amazon, and others, aim to provide global internet coverage but inadvertently emit electromagnetic radiation that interferes with scientific observations.
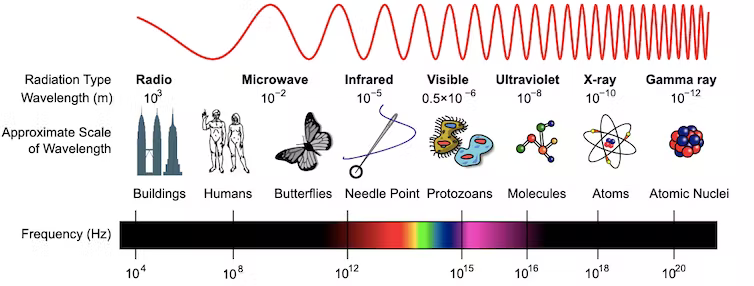
Of particular concern are the second-generation Starlink satellites—v2mini and v2mini Direct-to-Cell—which have been found to emit significantly more radiation than their predecessors. This radiation spans a broader spectrum of radio frequencies, encroaching into wavelengths critical for radio astronomy, notably between 150.05 and 153 megahertz (MHz). It is one of the remarkable revelations of the astronomical world in recent times and our Bacheors in Astronomy program at AIU is well-enriched with such innovations!
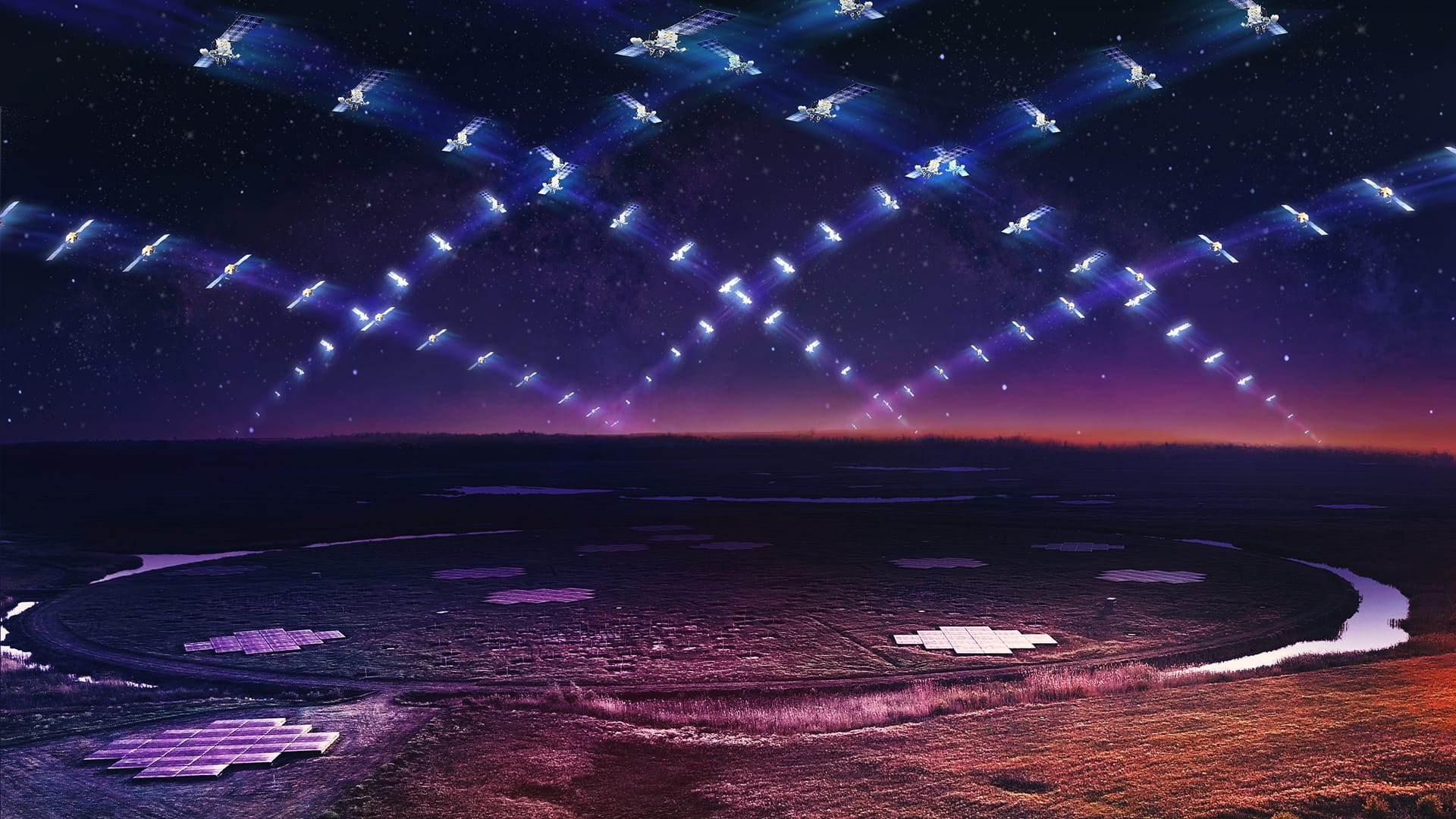

Radio astronomy relies on precise measurements within specific frequency bands to study celestial objects and phenomena such as pulsars, galaxies, and cosmic microwave background radiation. The unintended electromagnetic radiation emitted by satellite constellations, including Starlink, poses a serious threat by overwhelming these faint astrophysical signals. Researchers using instruments like the LOw Frequency ARray (LOFAR) in Europe have noted that the unintended emissions from these satellites can be up to 10 million times brighter than the faintest astronomical sources detectable by these radio telescopes. Such interference not only disrupts current observations but also jeopardizes the development of future radio astronomy technologies essential for space exploration and terrestrial applications like GPS and medical imaging.
Escalating Emission Levels: A Cause for Alarm
The escalation in satellite emissions underscores a pressing issue that demands immediate attention from both the scientific community and regulatory bodies worldwide. Despite assurances from companies like SpaceX about working on solutions, the pace of satellite deployment continues to outstrip regulatory responses. The lack of specific regulations addressing electromagnetic radiation leakage from satellite constellations exacerbates concerns as the number of satellites in low-Earth orbit continues to grow exponentially. Each new satellite launched contributes to a cumulative increase in the brightness of unintended emissions, further compromising the integrity of radio astronomy observations.
The consequences for radio astronomy are profound and multifaceted. Beyond the immediate disruption of observations, the long-term implications include hindering scientific advancements and potentially stalling discoveries in astrophysics. Radio astronomers rely on clear access to specific frequency bands to detect and study phenomena that reveal the fundamental workings of the universe. The interference from satellite emissions not only obscures these signals but also undermines efforts to refine instruments and techniques crucial for future discoveries. Moreover, the technologies developed for radio astronomy, such as high-frequency signal processing and data analysis, have far-reaching applications in communication systems, medical imaging, and beyond.
Regulatory Gaps and Calls for Action
The absence of comprehensive regulations addressing satellite radio pollution represents a critical gap in current space governance frameworks. While efforts to monitor and mitigate emissions are underway, they often lack enforceable mandates that compel satellite operators to minimize their impact on radio astronomy. The scientific community, represented by organizations like the Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy (ASTRON) and the SKA Observatory, urges regulatory bodies to establish clear guidelines that prioritize the protection of radio astronomy frequencies. Such regulations would not only safeguard ongoing research but also foster innovation in space technologies that can coexist harmoniously with scientific exploration.
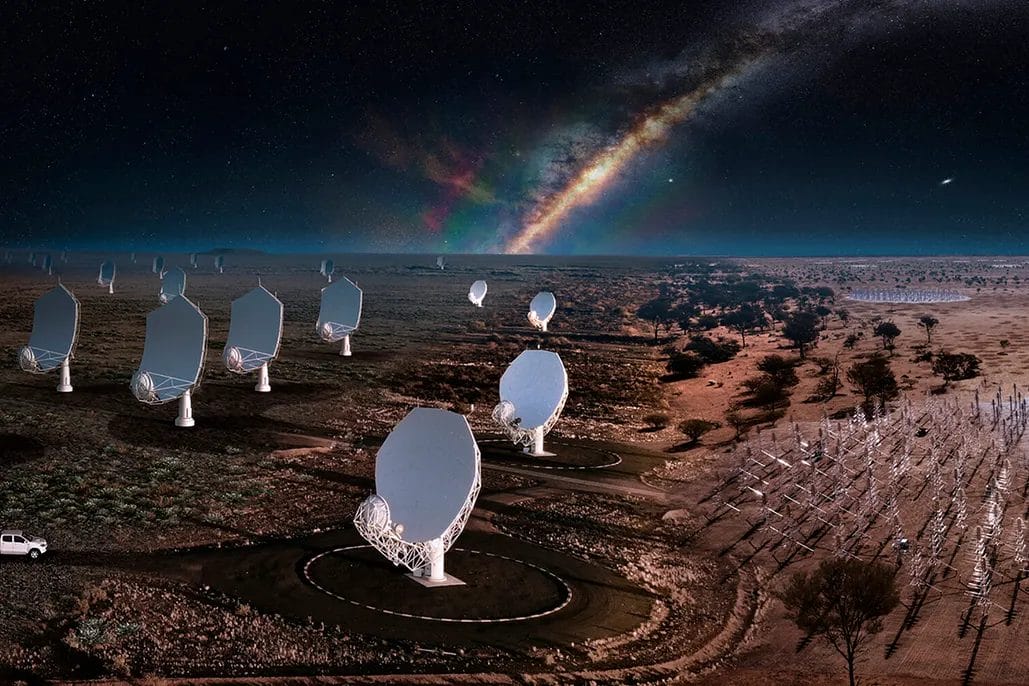

Efforts to address the regulatory gaps must be complemented by proactive measures within the industry. Acknowledging the gravity of the issue, satellite operators such as SpaceX have initiated programs to monitor and mitigate unintended emissions. However, the scale and rapid expansion of satellite constellations demand more robust and proactive measures. As industry leaders, these companies have a unique opportunity to set standards for responsible space operations. Collaborative efforts among satellite operators, scientists, and regulatory bodies are essential to developing and implementing effective solutions. These may include refining satellite design to reduce emissions and implementing real-time monitoring systems to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
The Way Forward: Collaboration and Innovation
Moving forward, concerted efforts are needed to strike a balance between technological advancement and environmental stewardship in space. By fostering collaboration between stakeholders and leveraging innovation in satellite design and regulatory frameworks, we can mitigate the adverse effects of satellite radio pollution on radio astronomy. The ongoing dialogue between scientists, policymakers, and industry leaders is crucial in shaping a sustainable future for space exploration and preserving the integrity of our window to the universe.
Preserving the ability to explore the cosmos through radio waves must remain a priority as humanity ventures deeper into space exploration and technological advancement. With concerted efforts and proactive measures, we can ensure that the night skies remain a pristine gateway to unraveling the mysteries of the universe. By addressing these challenges today, we pave the way for sustainable space exploration and uphold the invaluable contributions of radio astronomy to our understanding of the universe and its applications on Earth. Join AIU to explore more in-depth insights on this topic listed below.
Rescuing the commons as a space for true community participation by Tobias Roberts
Creating complex and precise models in space science
The Future of Space Exploration: Implications for the Global and Private Sectors
Human Space Exploration: Early Assessments of NASA’s Next Steps
Planetary Protection: Enabling Space Exploration While Safeguarding Against Biological Contamination
References
SpaceX’s Starlink Satellites Are Leaking More Radio Waves Than Ever
‘Worst nightmare’: Elon Musk’s Starlink satellites could blind radio telescopes
Reminder to our Dear Students,
Please ensure you are logged in as a student on the AIU platform and logged into the AIU Online
Library before accessing course links. This step is crucial for uninterrupted access to your learning
resources.
AIU Success Stories







Contact Us Today!
Begin Your Journey!
AIU’s Summer of Innovation and Growth gives you the ability to earn up to $5000 in tuition credit by completing free lessons and courses.
Whether you’re looking to acquire new skills, advance your career, or simply explore new interests, AIU is your gateway to a world of opportunities. With free access to 3400 lessons and hundreds of courses the ability to earn credits and earn certificates there’s no better time to start learning.
Join us today as a Guest Student and take the first step towards a brighter, more empowered future.
Explore. Learn. Achieve.

Contact Us
Atlantic International University
900 Fort Street Mall 905 Honolulu, HI 96813 [email protected]
Quick Links
Home | Online Courses | Available Courses | Virtual Campus | Career Center | Available Positions | Ask Career Coach | The Job Interview | Resume Writing | Accreditation | Areas of Study | Bachelor Degree Programs | Masters Degree Programs | Doctoral Degree Programs | Course & Curriculum | Human Rights | Online Library | Representations | Student Publication | Sponsors | General Information | Mission & Vision | School of Business and Economics | School of Science and Engineering | School of Social and Human Studies | Media Center | Admission Requirements | Apply Online | Tuition | Faculty & Staff | Distance Learning Overview | Student Testimonials | AIU Blogs | Register for Program | Privacy Policy | FAQ



















